Did you know that around 733 million people worldwide face hunger, and over 2.8 billion cannot afford a healthy diet?
Although the right to food is a basic human right, in Ghana, the situation of food insecurity worsened in 2022. The number of individuals in food crisis surged from 560,000 in 2021 to 823,000 in 2022, marking a 47% increase in individuals suffering from lack of food access, availability, and utilization.
WHAT IS FOOD INSECURITY?
It is the condition of not having access to sufficient food, or food of an adequate quality, to meet one's basic needs.
CAUSES OF FOOD INSECURITY
The main causes and drivers of food insecurity and hunger are poverty, environmental degradation (from illegal mining, increased urbanization and floods), food waste, high cost of living, food price inflation, conflict, and climate change (including the severe drought in Northern Ghana which has contributed to food insecurity in the country).
HEALTH EFFECTS OF FOOD INSECURITY
Food insecurity contributes to poor health, since people may skip meals, eat less, or switch to lower-quality foods.
Malnutrition can lead to weakness, pain, illness, and even death. Malnourished children have difficulty learning and may not develop properly. Food insecurity is associated with poor mental health, low educational attainment, and poor job performance.
Food insecurity also contributes to type 2 diabetes, obesity, and hypertension (high blood pressure) when less-expensive foods with lower nutritional value are substituted for healthy foods over the long term. Existing health issues can be worsened if people forgo necessary medication or medical treatment in order to buy food.
THE SOLUTIONS
The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization and the World, marks the World Food Day annually on 16th October to raise global awareness and encourages action for those suffering from hunger, emphasizing the importance of healthy diets for all.
Achieving this goal requires collective effort from all stakeholders along the food value chain.
Governments, supported by NGOs and academia, should implement policies fostering sustainable agriculture, including climate-resilient practices and encouraging local sourcing of raw materials. Food processing organizations should prioritize affordable nutrition.
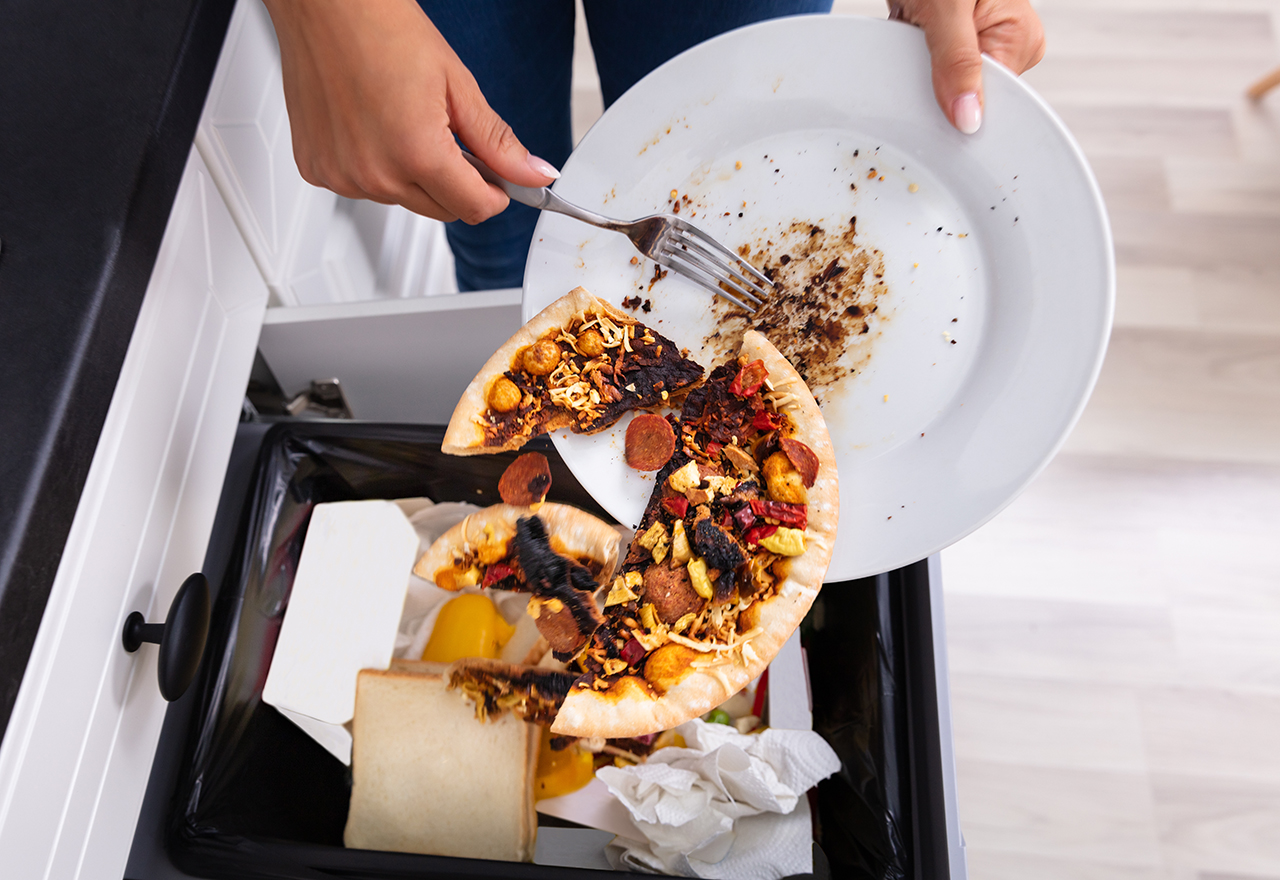

PRACTICAL WAYS TO PREVENT WASTAGE OF FOOD AT HOMES
• Buy food items in the required quantities only, especially perishable food.
• Avoid unnecessary cooking.
• Keep leftover food in the refrigerator.
• Try to reuse leftover by making new recipes.
• Keep a check of appetite before serving food; Plan your meals.
• Avoid serving too much food.
• Understand 'use by' vs 'best before' dates.
• Share extra food with others, particularly the vulnerable.
• Donate surplus food items to food banks and NGOs
BE INSPIRED TO TAKE ACTION TODAY TO ENSURE NO ONE IS LEFT BEHIND.
Authors: Elizabeth Mensah (Food Research & Development Technologist; Member, Aquafig Foundation) and Stephen R. Coleman (President, Aquafig Foundation).
1 State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI) Report - 2024 World Food Programme
2 Ghana: Inequalities in Food Insecurity, Prevalence of Food Insecurity in Ghana. FAOSTAT. https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FS
3 https://www.britannica.com/topic/food-insecurity
4 https://www.eufic.org/en/food-safety/article/how-to-reduce-food-waste-at-home
5 https://staging.afro.who.int/news/covid-19-could-deepen-food-insecurity-malnutrition-africa









